Difference between revisions of "WikipediaExtracts:Neoliberalism"
(Created by WPExtractsBot) |
m (Converted to use new extension InterwikiExtracts)) |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
''Extracted from Wikipedia'' -- | ''Extracted from Wikipedia'' -- | ||
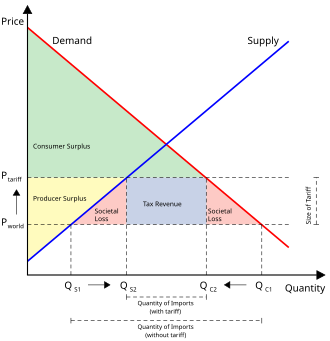
[[File:EffectOfTariff.svg|thumb]] | [[File:EffectOfTariff.svg|thumb]] | ||
| − | {{# | + | {{#InterwikiExtract: {{{1|{{PAGENAME}}}}} |
| + | |wiki=wikipedia | ||
| + | |format=text | ||
| + | |intro=true | ||
| + | }} | ||
Latest revision as of 21:47, 22 February 2022
Extracted from Wikipedia --
Neoliberalism is a political and economic ideology that advocates for free-market capitalism, which became dominant in policy-making from the late 20th century onward. The term has multiple, competing definitions, and is most often used pejoratively. In scholarly use, the term is often left undefined or used to describe a multitude of phenomena. However, it is primarily employed to delineate the societal transformation resulting from market-based reforms.
Neoliberalism is often associated with a set of economic liberalization policies, including privatization, deregulation, depoliticisation, consumer choice, labor market flexibilization, economic globalization, free trade, monetarism, austerity, and reductions in government spending. These policies are designed to increase the role of the private sector in the economy and society. Additionally, the neoliberal project is oriented towards the establishment of institutions and is inherently political in nature, extending beyond mere economic considerations.
Neoliberalism has become an increasingly prevalent term in recent decades. It has been a significant factor in the proliferation of conservative and right-libertarian organizations, political parties, and think tanks.
The term is rarely used by proponents of free-market policies. When the term entered into common academic use during the 1980s in association with Augusto Pinochet's economic reforms in Chile, it quickly acquired negative connotations and was employed principally by critics of market reform and laissez-faire capitalism. Scholars tended to associate it with the theories of economists working with the Mont Pelerin Society, including Friedrich Hayek, Milton Friedman, Ludwig von Mises, and James M. Buchanan, along with politicians and policy-makers such as Margaret Thatcher, Ronald Reagan, and Alan Greenspan. Once the new meaning of neoliberalism became established as common usage among Spanish-speaking scholars, it diffused into the English-language study of political economy. By 1994, the term entered global circulation and scholarship surrounding the topic has grown over the last few decades.
Neoliberalism originated among European liberal scholars during the 1930s. It emerged as a response to the perceived decline in popularity of classical liberalism, which was seen as giving way to a social liberal desire to control markets. This shift in thinking was shaped by the Great Depression and manifested in policies designed to counter the volatility of free markets. One motivation for the development of policies designed to mitigate the volatility of capitalist free markets was a desire to avoid repeating the economic failures of the early 1930s, which have been attributed, in part, to the economic policy of classical liberalism. In the context of policymaking, neoliberalism is often used to describe a paradigm shift that was said to follow the failure of the post-war consensus and neo-Keynesian economics to address the stagflation of the 1970s, although the 1973 oil crisis, a causal factor, was purely external, and created policy challenges that existing economic frameworks struggled to address.
According to multiple scholars the dissolution of the Soviet Union and the end of the Cold War have facilitated the rise of neoliberalism in the United States, the United Kingdom and around the world.